-Reagent.jpg)
-Reagent.jpg)
Chemelex S.A GPL Aso (with slide & Control) Reagent
(0 reviews)
Sold by:
Inhouse product
Inhouse product
Price:
৳3,200.00
/PC
Share:
Top Selling Products
-
Soundless Dental compressor
৳15,300.00 -
Dental Curing Light 100A Tulip
৳3,150.00 -
CHEM-7 Semi Auto Bio Chemistry Analyzer
৳195,000.00 -
ntfs beauty facial steamer
৳1,199.00
Chemelex S.A GPL Aso (with slide & Control) Reagent
The ASO titer tends to rise a week following infection and peaks at 3 to 5 weeks, begins to fall at 8 weeks, and returns to preinfection levels at around 8 months. Stronger ASO responses tend to occur with throat infection than skin infection, possibly because free cholesterol present in skin binds to streptolysin O, thereby decreasing its immunogenicity. Qualitative and semi-quantitative determination of anti-streptolysin-O antibodies (ASO) in serum can be performed using a rapid latex agglutination test.
There have been no reviews for this product yet.
Related products
৳1,000.00
Chemelex S.A GPL Typhi para AO/B-O
৳4,000.00
Chemelex Widal Kit, AH BHTH , To
৳1,400.00
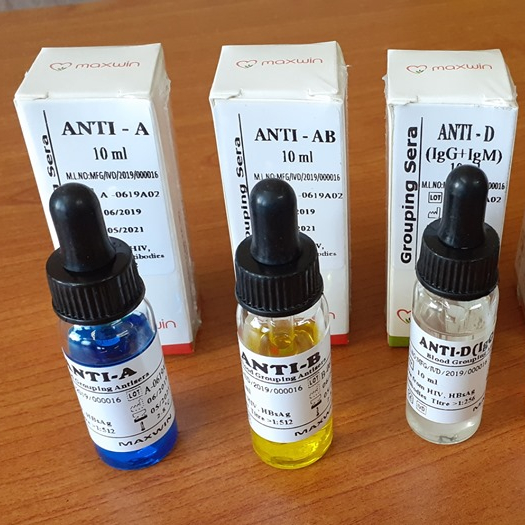
Chemelex S.A GPL BloodmGrouping Set
৳35,000.00
Chemelex S.A GPL Pregnancy Latex Only
৳2,500.00




.png)






-Reagent.jpg)

